Topographic control of the Gulf Stream
Gulf Stream along the U.S. Seaboard
The Gulf Stream strongly interacts with the topography along the U.S. Eastern Seaboard, between the Straits of Florida and Cape Hatteras. Dynamics of the Gulf Stream in this region are investigated with a set of realistic, very high resolution simulations using the oceanic model ROMS in [1].
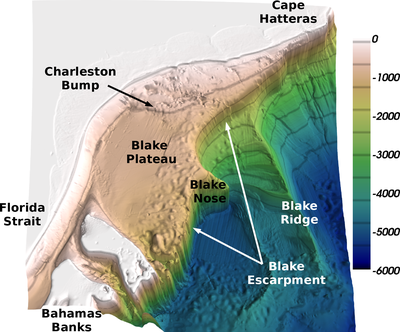
The mean path is strongly influenced by the topography and in particular the Charleston Bump.
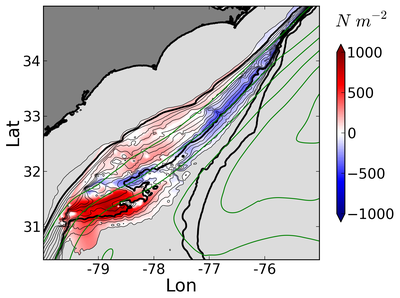
There are significant local pressure anomaly and topographic form stress exerted by the Bump that retard the mean flow and steer the mean current pathway seaward.
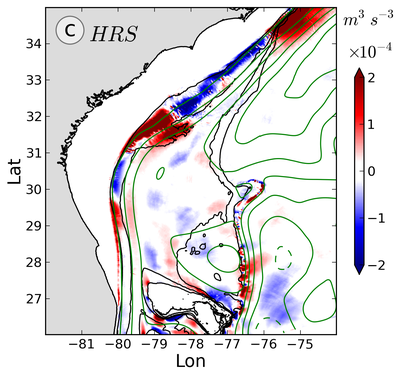
The effect of the topography on the development of meanders and eddies is studied by computing energy budgets of the eddies and the mean flow. The baroclinic instability is stabilized by the slope everywhere except past the Bump. The flow is barotropically unstable, and kinetic energy is converted from the mean flow to the eddies following the Straits of Florida and at the Bump with regions of eddy-to-mean conversion in-between. The pattern of eddy fluxes is interpreted in terms of eddy life cycle, eddy fluxes being directed downgradient in eddy growth regions and upgradient in eddy decay regions.
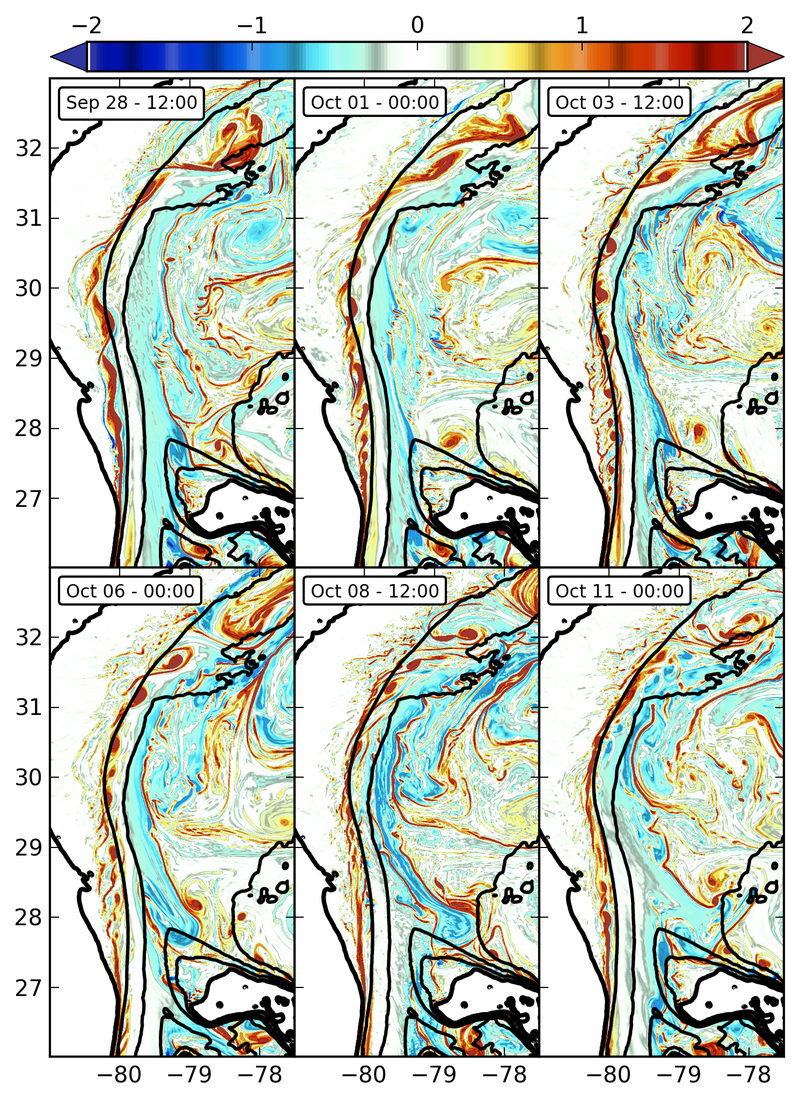
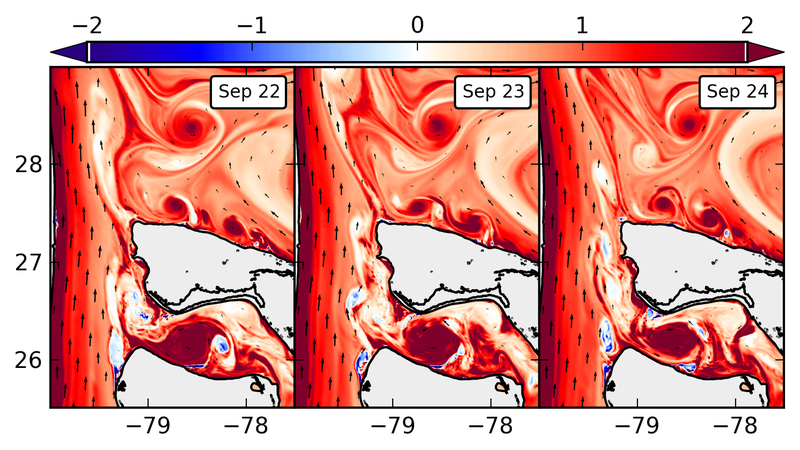
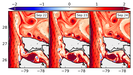
Snapshots of surface relative vorticity normalized by f (colors). Barotropic instability of the flow is visible between the Florida Straight and the Charleston Bump in the form of a cyclonic vortex street.
The cyclonic shear is amplified by bottom drag along the Florida coast, releases its energy through horizontal Reynolds stress when the flow moves away from the slope, and rolls up into a street of submesoscale vortices. These vortices are amplified at the Bump due to mixed barotropic-baroclinic instability processes that lead to the formation of intense mesoscale slope eddies.
Movie
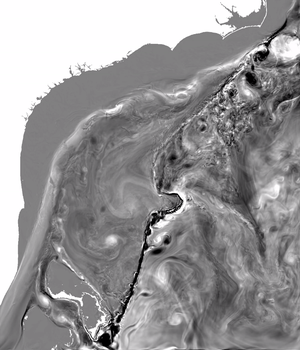
1 year of barotropic vorticity from a 750 m resolution ROMS simulation of the Gulf Stream along the Seaboard [.mov ]
Bibliography
| [1] | J. Gula, J. Molemaker and J.C. McWilliams (2015)
Gulf Stream dynamics along the Southeastern U.S. Seaboard.
J. Phys. Oceanogr., 45, 690-715.
|
| [2] | J. Gula, J. Molemaker and J.C. McWilliams (2015)
Topographic vorticity generation, submesoscale instability and vortex street formation in the Gulf Stream
Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 4054-4062.
|
| [3] | J. Gula, J. Molemaker and J.C. McWilliams
Topographic generation of submesoscale centrifugal instability and energy dissipation
Submitted
|